Introduction:
The Geolocation API gives a location and accuracy radius based on cell tower and WiFi node information detected by the mobile client. The protocol used to deliver this data to the server and return a response to the client is described in this document.
POST is used for HTTPS communication. Both the request and the answer are in JSON format, with the content type application/json.
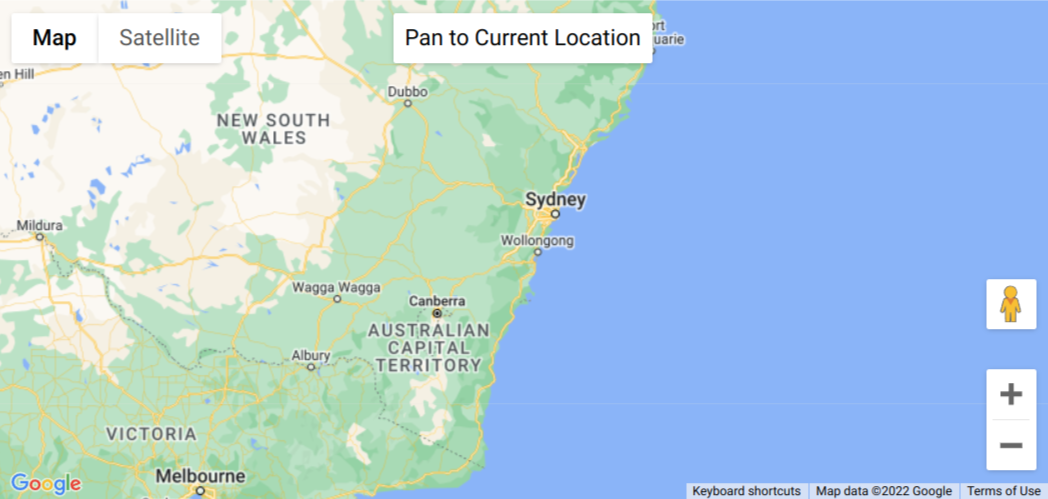
This example creates a map that displays the geographic location of a user or device on a Google map, through use of their browser’s HTML5 Geolocation feature. The user must consent to location sharing or else an error is shown.
Code:
let map: google.maps.Map, infoWindow: google.maps.InfoWindow;
function initMap(): void {
map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement, {
center: { lat: -34.397, lng: 150.644 },
zoom: 6,
});
infoWindow = new google.maps.InfoWindow();
const locationButton = document.createElement("button");
locationButton.textContent = "Pan to Current Location";
locationButton.classList.add("custom-map-control-button");
map.controls[google.maps.ControlPosition.TOP_CENTER].push(locationButton);
locationButton.addEventListener("click", () => {
// Try HTML5 geolocation.
if (navigator.geolocation) {
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(
(position: GeolocationPosition) => {
const pos = {
lat: position.coords.latitude,
lng: position.coords.longitude,
};
infoWindow.setPosition(pos);
infoWindow.setContent("Location found.");
infoWindow.open(map);
map.setCenter(pos);
},
() => {
handleLocationError(true, infoWindow, map.getCenter()!);
}
);
} else {
// Browser doesn't support Geolocation
handleLocationError(false, infoWindow, map.getCenter()!);
}
});
}
function handleLocationError(
browserHasGeolocation: boolean,
infoWindow: google.maps.InfoWindow,
pos: google.maps.LatLng
) {
infoWindow.setPosition(pos);
infoWindow.setContent(
browserHasGeolocation
? "Error: The Geolocation service failed."
: "Error: Your browser doesn't support geolocation." );
infoWindow.open(map);
}
declare global {
interface Window {
initMap: () => void;
}
}
window.initMap = initMap;
export {};
Explanation:
- The function initMap() is created for setting the properties of the map.
- The line, “map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById(“map”)”; creates a new map inside the <div> element with the help of the mentioned id which is ‘map’ as an HTMLElement.
map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement,
- The ‘centre’ attribute defines where the map should be centered with the help of the latitude and longitude coordinates).
center: { lat: -34.397, lng: 150.644 },
- The ‘zoom’ attribute specifies the map’s zoom level.
zoom: 6,
- Next, the new InfoWindow() is created.
infoWindow = new google.maps.InfoWindow();
- The variable locationButton is created; the createElement() method creates an element node.
- Map controls are mentioned as the Top_center.
map.controls[google.maps.ControlPosition.TOP_CENTER].push(locationButton);
- Next, the addEventListener is created to add the click option for the users.
locationButton.addEventListener("click", () => { }
- The HTML5 geolocation is then tried/navigated and if browser doesn’t support the geolocation, then the error is shown.
- Followed by this, the function to handle the location error is created.
function handleLocationError(
browserHasGeolocation: boolean,
infoWindow: google.maps.InfoWindow,
pos: google.maps.LatLng
) {
infoWindow.setPosition(pos);
infoWindow.setContent(
browserHasGeolocation
? "Error: The Geolocation service failed."
: "Error: Your browser doesn't support geolocation."
);
infoWindow.open(map);
}
- Lastly, the function is called and executed.
window.initMap = initMap;
Conclusion:
Thus, in this tutorial we learned how to show the geolocation of the user. This example created a map that displays the geographic location of a user or device on a Google map, through use of their browser’s HTML5 Geolocation feature. The user must consent to location sharing or else an error is shown.

Recent Posts
Loading recent posts...